Smart agriculture isn’t just a buzzword; it’s a game-changer. Take, for instance, the smart greenhouse. Gone are the days of relying solely on the whims of nature. Now, with the power of IoT, these green sanctuaries become veritable hubs of efficiency and productivity. Sensors embedded in the soil monitor moisture levels, ensuring that crops receive just the right amount of hydration. Meanwhile, temperature and humidity sensors maintain optimal growing conditions, mimicking Mother Nature’s gentle touch.
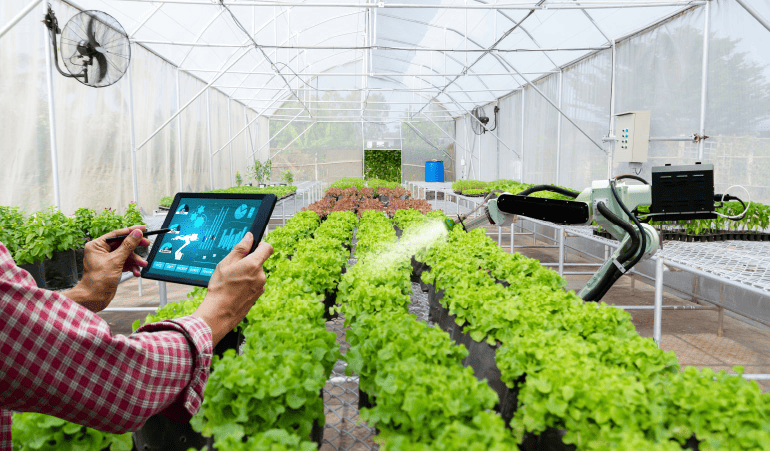

Picture this: a bustling greenhouse, brimming with lush greenery, where technology orchestrates a symphony of growth. Welcome to the world of automated greenhouse systems, where innovation meets cultivation to revolutionize the way we farm. By seamlessly integrating sensors, actuators, and other smart devices, this cutting-edge approach transforms traditional farming into a high-tech, data-driven endeavor.
But the magic doesn’t stop there. Smart actuators swing into action, adjusting shades and ventilation systems to regulate light and airflow. This meticulous orchestration of environmental variables ensures that each plant thrives, maximizing yield and quality. Imagine tomatoes ripening to perfection under the watchful eye of intelligent systems, or delicate herbs flourishing in a carefully curated microclimate.
Yet, the true beauty of IoT-based smart agriculture lies not just in its technological prowess, but in its commitment to sustainability. By harnessing the power of data and automation, farmers can implement eco-friendly practices with unprecedented precision. For example, by monitoring soil moisture levels in real-time, excessive irrigation can be avoided, reducing water wastage and preserving this precious resource. Similarly, by fine-tuning climate control systems, energy consumption is optimized, minimizing the carbon footprint of greenhouse operations.
Moreover, smart agriculture enables proactive pest management and disease prevention. By deploying sensors that detect early signs of infestation or plant stress, farmers can intervene swiftly and precisely, minimizing the need for chemical pesticides and herbicides. This not only safeguards the health of the crops but also promotes biodiversity and ecosystem resilience.
IoT-based smart agriculture isn’t just about growing crops; it’s about cultivating a sustainable future. It’s about harnessing the power of technology to nurture our planet while feeding a growing population. So, the next time you step into a greenhouse, take a moment to marvel at the marvels of modern farming – where tradition meets innovation, and sustainability blossoms in every leaf. Welcome to the green revolution of tomorrow.
Tips To Automate Greenhouse With IoT
Greenhouse cultivation significantly boosts crop yields for various produce. Typically, greenhouses manage environmental conditions either manually or through proportional control mechanisms. However, manual intervention presents drawbacks like decreased productivity, energy wastage, and higher labor expenses, making it less efficient. In contrast, smart greenhouses equipped with IoT technology offer a smarter alternative. These systems not only monitor environmental factors with precision but also regulate them autonomously.
This eliminates the necessity for human involvement in greenhouse operations. By employing IoT-embedded systems, smart greenhouses optimize conditions such as temperature, humidity, and light levels, ensuring ideal growing environments for different crops. Consequently, farmers can mitigate losses associated with manual adjustments and enhance overall productivity. With IoT-enabled automation, greenhouses operate seamlessly, maximizing efficiency and reducing operational costs while minimizing human intervention. All this can be carried by following these tips:
1. Implement Sensor Networks
Set up a network of sensors throughout the greenhouse to monitor environmental parameters such as temperature, humidity, light levels, soil moisture, and CO2 levels. These sensors provide real-time data that forms the basis for automated decision-making. Analytic farming is a forewarning which can help in strategic decisions. For instance
Predictive analytics in farming can anticipate pest outbreaks based on weather patterns, enabling farmers to deploy preventive measures like organic sprays, reducing crop damage and ensuring higher yields.
2. Utilize Actuators for Control
Install actuators such as motorized vents, fans, and shades to control the greenhouse environment based on the data collected by sensors. Actuators can adjust ventilation, shading, and temperature to maintain optimal growing conditions for different crops. A Conducive environment through controlled methods is not exactly meddling with nature. It is the only way of getting our basics right about how the plant would yield in the best possible conditions.
3. Integrate IoT Platform
Choose an IoT platform or software that can collect, analyze, and manage data from the sensors and actuators in the greenhouse. This platform should provide a user-friendly interface for setting up automation rules and monitoring the greenhouse remotely.
4. Set Up Automated Irrigation Systems
Implement automated irrigation systems that deliver water to plants based on their specific needs. Soil moisture sensors can trigger irrigation cycles, ensuring that plants receive the right amount of water without wastage.
5. Implement Climate Control Algorithms
Develop algorithms that use sensor data to control climate parameters such as temperature and humidity. These algorithms can adjust ventilation, heating, and cooling systems to maintain ideal growing conditions for different crops throughout the day and night.
6. Introduce Remote Monitoring and Control
Enable remote monitoring and control of the greenhouse systems using IoT-enabled devices such as smartphones, tablets, or computers. This allows farmers to keep an eye on their crops and make adjustments to the automation settings from anywhere with an internet connection.
7. Integrate Predictive Analytics
Incorporate predictive analytics into the IoT platform to forecast environmental conditions and crop growth patterns. By analyzing historical data and trends, predictive analytics can help farmers make informed decisions about planting schedules, crop rotation, and pest management.
8. Implement Energy Optimization Strategies
Optimize energy usage in the greenhouse by scheduling automation tasks to run during off-peak hours when electricity prices are lower. Additionally, consider integrating renewable energy sources such as solar panels to power IoT devices and reduce reliance on the grid.
- RELATED – The evolution of embedded GUI development over the last decade
- 5 Advantages For Using eContracts Over Traditional Contracts
Conclusion:
As years of pollution continue to alter the climate, the reality of these changes becomes increasingly evident. In response, controlled greenhouses with automated features emerge as a vital alternative for sustainable agriculture. By harnessing technology to regulate environmental conditions, these greenhouses offer a solution to mitigate the adverse effects of climate change on crop cultivation. Embracing this approach not only ensures consistent yields but also promotes resource efficiency and resilience in the face of evolving environmental challenges.
I hope this tutorial helped you to know about “Tips to Enable Greenhouse Automation using IoT”. If you want to say anything, let us know through the comment sections. If you like this article, please share it and follow WhatVwant on Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube for more Technical tips.
Tips to enable Greenhouse Automation using IoT – FAQs
How IoT can help in greenhouse control?
IoT applications help monitor environmental factors like temperature, humidity, light, air quality, and soil moisture.
What are the advantages of IoT based greenhouse monitoring system?
One of the primary benefits of IoT-driven greenhouse monitoring is the ability to collect real-time data on crucial environmental parameters.
What sensors are used in automated greenhouses?
Both capacitive and resistive solid-state sensors are fairly common in greenhouses because they offer reasonable accuracy and, in the humidity range typical of most horticulture applications, maintenance is generally limited to cleaning once or twice per year.
How can IoT solve climate change?
IoT can help improve transportation, routing, traffic congestion, parking solutions, and many other areas related to commuting.
How IoT is used in renewable energy?
IoT solutions help companies leverage renewable energy solutions and ensure their efficiency.