The first section of this article covers the fundamentals of Augmented reality (AR), including what it is and how it functions. Then, using numerous examples, we’ll examine the principal uses of augmented reality, including manufacturing, health care, gaming, education, and remote collaboration. We will also discuss augmented reality-related technology, software, apps, and equipment. This article will also discuss the commercial prognosis for augmented reality and the problems and difficulties related to the many expanded reality themes.
What is Augmented reality?

Let us understand the meaning or definition of augmented reality in detail before diving further
The real-time integration of digital information with the environment of the user is known as augmented reality (AR). Users of augmented reality (AR) encounter a real-world environment with created perceptual information superimposed on top of it, as opposed to virtual reality (VR), which produces a completely artificial environment.
Using augmented reality, users can receive more information or have natural environments aesthetically altered in some way. The main advantage of augmented reality (AR) is that it successfully combines digital and three-dimensional (3D) elements with how people perceive the real world. AR has several applications, from entertainment to aid in decision-making.
With a device like a smartphone or glasses, augmented reality (AR) provides the user with visual elements, sound, and other sensory information. To provide a seamless experience where digital information modifies the user’s view of the actual environment, this information is layered onto the device. A part of the natural world might be hidden or added to by the superimposed information.
On the other hand, there are wearable gadgets that enable users to watch augmented reality content. AR glasses do not fully immerse users in virtual worlds like virtual reality headsets do. The wearers of the glasses can add to or overlay a virtual object on a real-world object, such as placing augmented reality (AR) markings on machines to indicate repair areas.
The yellow first down marker that started to appear in televised football games sometime in 1998 was one of the first commercial uses of augmented reality technology. The most well-known consumer augmented reality (AR) devices right now include Google Glass, smartphone games, and heads-up displays (HUDs) on automobile windscreens. But a lot of other businesses, like healthcare, public safety, gas and oil, travel, and marketing, also employ technology.
Elements of AR
We have 3 major elements in AR which support it’s entire working and other operations they are:
- Hardware
- Software
- Remote server
1. Hardware

The hardware for augmented reality systems includes CPUs, input devices, sensors, and displays. These are tiny wearable devices that contain micro supercomputers. They have many different parts, including a CPU, flash memory, RAM, GPS, GPU, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth, and they need a lot of processing power.
The processor receives information from sensors outside the augmented reality device about how the user interacts with objects in the outside environment. These sensors may be the accelerometer, infrared, or gyroscope on a mobile device.
Outside the apparatus, cameras are also positioned to scan the environment and gather pertinent data. The instruments that create digital models for determining the right output use this information. Mirrors are also employed to improve how our eyes perceive virtual images.
While just a few augmented reality gadgets are equipped with a variety of tiny curved mirrors, very few others include double-sided mirrors. This mirror has a surface that bounces light from an eyepiece display onto a camera, and another surface that bounces light from a side-mounted display onto the eye. A mobile device, monitor, head-mounted displays (HMD), or spectacles can all serve as a display.
2. Software

The software has a significant impact on how augmented reality devices work. Applications based on augmented reality are developed using D’Fusion and other specialized 3D software. Virtual graphics that cover the real-world image are created using 3D software. A few of these include StudioMax, AutoCad3D, and Cinema 4D.
3. Remote Server
A database for the virtual images scanned is kept up to date using a cloud or web server in addition to the software and hardware. Virtual images will be retrieved from the database and sent to the requesting application in response to requests from the augmented reality applications.
Advantages of AR
Let us go through some of the essential advantages and applications of AR
- As gaming environments shift from virtual realms to incorporate real-life experiences where players can engage in real-life activities to play, AR enables improved gaming experiences.
- In the retail industry, customers can use a store’s internet app to virtually tour furnishings before making a purchase.
- Ads can be incorporated into AR material to assist businesses to make their content more widely known to viewers. AR can enhance customer experiences by displaying 3D models of things to customers and assisting them in making better decisions by providing them with virtual tours of products, such as those seen in real estate.
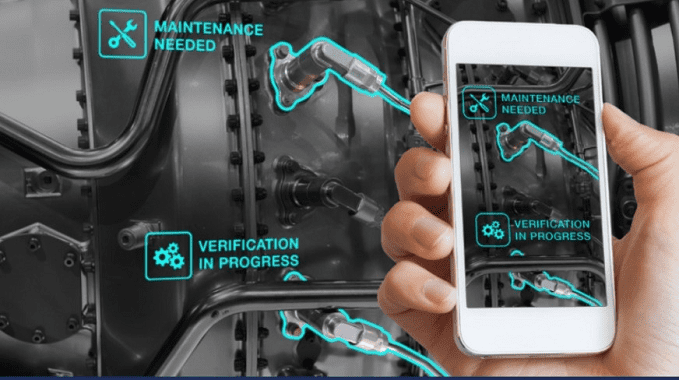
- Without the need for specialists to come to the spot, repair technicians can be instructed remotely to perform repairs and maintenance tasks while on the ground utilizing AR apps. This can be helpful in areas when getting to the destination is challenging.
- In education, augmented reality is utilized to create a common curriculum. The student’s actual environment can be overlaid with graphics, text, music, and video. It has made it possible for pupils to employ interactive reading resources that provide them with more information.
- AR helps mark objects in real-time and aids in advanced navigation. Data that shows destination directions, travel times, weather information, and road conditions can be shown on a car’s windscreen.
- AR can be used for navigation, offering information on locations, directions, and sightseeing, in addition to the placement of advertisements on AR material.
- Remote training, health situation monitoring, and patient diagnosis can all be aided by augmented reality. The surgeons are receiving patient data through augmented reality. Additionally, it enables the acquisition and overlay of functional videos and patient imaging records. It is utilized during operations, recuperation procedures, and hands-on training sessions.
- Related: What are the Advantages of a Good NFT Design?
- 5 Advantages Of Using A Timeline Maker For Project Monitoring
Disadvantages of AR
As we had gone through the advantages of AR now Let us also go through some of the Disadvantages of AR
- The creation and upkeep of AR technology-based initiatives are expensive. In addition, making AR-based gadgets is expensive.
- Loss of privacy in AR-based apps is a worry.
- People in AR are losing out on significant events.
- The poor performance level is a worry that needs to be addressed throughout the testing process, and using AR-compliant devices efficiently necessitates some basic training.
Types of AR
Let us go through the types of AR, essentially we have four important types of AR,
- Marker-based
- Marker-less
- Projection-based
- Superimposition-based AR
Let us go through each of the AR types mentioned above in detail
1. Marker-based AR

Target images (markers) are used in marker-based AR applications to position items in an area. These markers specify where the 3D digital content will be displayed inside the user’s field of view. Markers served as the foundation for early AR technologies.
To superimpose the 3D virtual object on a particular physical picture pattern marker in a real-world context, these applications are connected to it. To generate its geometry, the cameras must continuously scan the input and set a marker for picture pattern recognition. The virtual object won’t appear if the camera is not correctly focused.
As a result, a system for marking images includes several modules, including a camera, image capture, image processing, and marker tracking, among others. Generally speaking, this is a straightforward and low-cost method to include filters through a unique program to recognize particular patterns through a camera.
Instagram and Snapchat use this kind of augmented reality through their filters and games as an example. As a result, this kind of AR has already been incorporated into people’s daily lives because they are common social activities.
2. Marker-less AR

By comparing the features existing in the data in real-time, markerless AR, in contrast, enables the positioning of virtual 3D objects in the real image environment. While the augmented reality software does the rest, this kind of assistance depends on the technology of every smartphone, including the camera, GPS, and accelerometer, among others.
The absence of an object-tracking system in this model is a result of current advancements in cameras, sensors, and AI algorithms. As a result, it operates using the digital information gathered by these sensors, which can capture a physical location in real time.
Simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) is the primary tool used in markerless analysis to scan the environment and provide suitable maps for the placement of virtual objects. Even if the virtual items are not within the user’s field of view, they do not move when the user moves, and the user does not need to scan new photos, SLAM markerless image tracking scans the surroundings and develops maps of where to place the virtual objects in 3D.
Because of this, this technology may recognize items or distinguishing features in a scene without being aware of its surroundings, such as walls or intersections. This technique is distinguished by its connection to the striking visual result of fusing computer graphics with actual photographs.
The technology employs location-based information to determine what material the user gets or discovers in a certain area and is used in events, business, and navigation apps, for example. As with mobile phones, it might use accelerometers, gyroscopes, compasses, and GPS.
3. Projection-based AR

This technology is used to transmit digital data in a static environment; project-based augmented reality, for example, focuses on presenting virtual 3D objects in the user’s actual environment.
Due to the placement of a tracking camera and a fixed projector in a particular location, augmented reality (AR) enables the user to move freely inside the surroundings of that space. By projecting artificial light onto actual flat surfaces, this technique primarily serves to produce illusions regarding the depth, position, and orientation of an object.
Because instructions may be presented in a specific region, projection-based augmented reality, for instance, is excellent for streamlining complex activities in commerce or industry and removing computers. Also, by providing feedback, this system can optimize digital identification procedures for manufacturing cycles.
4. Superimposition-based AR

Superimposition-based AR offers an “alternative” view of the object in question by either completely replacing the original view with an augmented view of the object or only partially replacing it. Once again, object recognition is crucial in this situation since, logically, the program cannot replace the original view with an enhanced one if it doesn’t know what it is looking at.
In this instance, an augmentation may completely or partially replace the original object. In the example below, users of the IKEA Catalog app can scale a virtual piece of furniture and place it over an image of a room.
Applications for superimposition augmented reality include gaming, entertainment, education, and industrial design. Superimposition AR, for instance, can be used to develop interactive games that let players play in real-world settings or view and interact with 3D models in real time while designing.
Superimposition AR technology, in general, offers an interesting and new approach to combining virtual and real-world surroundings, and it is anticipated to play a larger part in a variety of future sectors.
- Related:5 Biggest Tech Breakthroughs of the Last Decade
- 11 Most Popular Latest Gadgets In The Market
Equipment used in AR
A range of tools and gadgets are necessary for the operation of augmented reality (AR) technology. Among the most important tools and gadgets used in AR are the ones listed below:
- Display devices: To present virtual things in the actual environment, AR applications need some sort of display device. These gadgets can include head-mounted displays like AR glasses as well as portable electronics like smartphones and tablets.
- Cameras: To feed the AR system with photos of real-world surroundings, cameras are utilized to capture them. They may be external or integrated into a device.
- Sensors: To determine the orientation, movement, and location of the user or the device, sensors like accelerometers, gyroscopes, and GPS are utilized. The virtual objects are positioned in the physical world using this information.
- Powerful processors are necessary for real-time picture processing and data analysis in AR systems. These processors may be integrated into a product or housed in a network based in the cloud.
- Software development resources: Software development kits (SDKs) for augmented reality (AR) give developers the resources they need to make AR applications. These SDKs could come with libraries, APIs, and development utilities.
- Tracking systems: To properly track the position and orientation of the device and the user in the real world, tracking systems including fiducial markers, location-based markers, and sensor-based tracking systems are utilized.
- Haptic devices: Haptic devices provide tactile feedback to give the user a more immersive experience with augmented reality.
Depending on the type of application and amount of immersion required, several tools and gadgets are utilized in augmented reality. We can anticipate additional tools and equipment that improve the AR experience as the technology develops.
- Related: How to Migrate Or Backup Oculus Rift Data?
- CyberLink PowerDVD 18: Best Movie and Media Player
Augmented reality apps

Apps that use augmented reality (AR) technology to build a digital overlay over the physical world are known as augmented reality (AR) apps. These apps give consumers a simple and easy way to interact with virtual objects and information.
Let us go through some of the essential apps of Augmented reality
- Pokémon Go: This is an AR-enhanced mobile game that allows users to capture and engage in real-world combat with virtual Pokémon.
- Snapchat: is a social media software that lets users add various augmented reality (AR) filters and lenses to their faces and the environment around them, enabling them to capture original and funny videos and images.
- Google Translate: An application called Google Translate employs augmented reality to instantly translate text. The program will translate any written content into the desired language when users point their camera at a sign, menu, or another piece of writing.
- IKEA Place is an app that lets users place virtual versions of IKEA furniture in real-time using the camera on their smartphone to see how it would look in their house.
- Quiver: A learning application that employs augmented reality to make coloring books come to life. The program recognizes the image when users color the pages and overlays a 3D animation over it.
- Holo: With the help of the app Holo, users can install 3D holograms of various items anywhere in the real world to create fun and engaging experiences.
- Civilizations AR: An educational software called Civilizations AR employs augmented reality (AR) technology to provide interactive exhibits of historical artifacts and occasions, enabling users to understand history in a more engrossing and immersive manner.
These are just a few of the numerous AR apps that are accessible on different platforms. Future AR applications are likely to be even more creative and interesting as AR technology develops.
Best AR development platforms
Developers can choose from a wide variety of augmented reality (AR) development platforms. Some of the top AR development platforms at this time are listed below:
- ARKit: Apple’s ARKit development framework enables the creation of augmented reality (AR) software for iOS devices. For iOS users, ARKit’s features, such as plane detection, illumination estimation, and motion tracking, make it simple to build AR experiences.
- ARCore: Google’s ARCore development framework enables the creation of augmented reality (AR) applications for Android smartphones. It is simple to create AR experiences for Android users thanks to ARCore’s motion tracking, environmental comprehension, and light estimation features.
- Vuforia: PTC’s Vuforia is an AR development platform that enables programmers to make AR applications for smart glasses and mobile devices. Complex and immersive AR experiences are simple to make because of Vuforia’s features, which include picture recognition, 3D object recognition, and spatial recognition.
- Wikitude: Wikitude is a platform for building augmented reality (AR) applications that can be used with web browsers, smart glasses, and mobile devices. Wikitude makes it simple to develop a variety of AR experiences by offering tools like picture recognition, location-based AR, and object detection.
- Unity: A well-known game engine that also facilitates the creation of augmented reality. Developers may design AR experiences that work on desktop and mobile platforms with the aid of Unity. Unity is a potent AR creation platform since it offers features including 3D modeling, physics simulation, and audio and video rendering.
- Maxst: A platform for developing augmented reality applications, Maxst offers features including 3D object identification, immediate tracking, and image recognition. Maxst enables developers to rapidly and easily create AR experiences on both the Android and iOS platforms.
These are only a few of the top AR development tools that are currently accessible. The best platform to use will depend on the particular needs of the AR application being created.
- Related: What is Autodesk & List of Autodesk Products
- How to recover deleted files from Windows, Mac, iPhone, USB, etc.,
Conclusion :
We discovered through this augmented reality that technology enables the superimposition of virtual items over real-world environments or objects. It uses a variety of technologies, including object recognition, depth tracking, SLAM, and natural feature tracking, among others. This augmented reality tutorial focused on introducing AR, outlining its fundamental principles, outlining its technology, and discussing its applications. The optimal approach for individuals interested in integrating and creating AR was the last thing we thought about.
I hope this tutorial helped you with Augmented reality: The Complete details. If you want to say anything, let us know through the comment sections. If you like this article, please share it and follow WhatVwant on Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube for more Technical tips.
- Related:7 Types of Virtual Reality Games in the Real World
- How AR, VR, and Mixed Reality can help Education
- Which technologies will be in demand in the future?
Augmented reality – FAQs
What is a good illustration of augmented reality?
In order to improve the experience, augmented reality overlays virtual data or even a virtual world on top of the already existing real-world surroundings. Consider Pokémon Go as an illustration, where players look for animated characters that appear in their real-world surroundings on their phone or tablet.
Compare AI and AR.
While AR and VR involve some form of interaction with the physical world, AI involves computer systems discovering ways to resolve user problems on their own. Machine learning involves digesting vast volumes of data, discovering correlations, and developing decision-making skills.
What distinguishes AR from VR?
Unlike VR, which is entirely virtual, AR leverages a real-world environment. While VR users are under the system’s supervision, AR users have some influence over their presence in the actual world. AR can be accessed with a smartphone, whereas VR needs a headgear device. In contrast to virtual reality, augmented reality (AR) improves both the actual and virtual worlds.
Python is used in AR?
According to a survey done between late 2021 and early 2022, Python was closely followed by JavaScript as the most popular coding language used by software developers in augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) projects.
